 Arrays are extremely important theme in C ++. The programs are used very often and understand the subject must be thoroughly. Immediately you will please – to understand and learn how to use arrays is simple enough even a beginner.
Arrays are extremely important theme in C ++. The programs are used very often and understand the subject must be thoroughly. Immediately you will please – to understand and learn how to use arrays is simple enough even a beginner.
So, why do we need arrays and what they look like? By now you already know well, that the program data is stored in the declared us variables of a certain type (int, double, char… ). But it so happens, that the program needs to store hundreds of (and even more) variables of the same type of data, as well as the need to work with them - assign values, modify them, etc..
For example, it is necessary to store the serial numbers of rows. Agree – anyone would be scared by the thought, it is necessary to create a hundred of type int variables, give each a unique name, and assign a value from 1 to 500-ta. (I'm scared already :) In this case, We simply save arrays.
Note the ground and move on to the practical example:
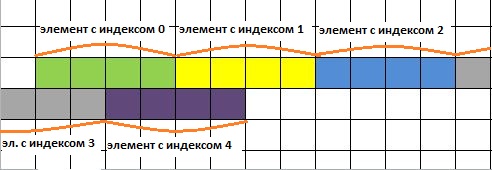
- an array in c ++ is the sum of a certain number of one-type variables, with the same name. For example, int array [3];. This entry means, we declared an array named array , which thecontains 3 type variables int;
- array variables are called elements ;
- Each element has its own unique code - a sequence number. Using the index, we can refer to a specific element. IMPORTANT - indexing array elements begins with 0. So in an array int array [3] the first element has index 0, and the last - 2. To contact, for example, to the zero element of the array and change its value, it is necessary to specify the name of the array in square brackets to indicate the index– array [0] = 33.
Consider the example:
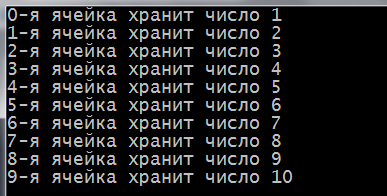
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // в этой программе создаем массив с размером size, // с помощью цикла for вносим данные во все ячейки // массива и отображаем их содержимое на экран #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); const int SIZE = 10; //объявляем константу int firstArray[SIZE ]; //объявляем массив с количеством элементов SIZE for (int i = 0; i < SIZE ; i++) //заполняем и отображаем значения на экран { firstArray[i] = i + 1; // на первом шаге цикла firstArray[0] присвоить 1 (0 + 1) cout << i << "-я ячейка хранит число " << firstArray[i] << endl; } cout << endl; return 0; } |
In line 12, we define an integer constant SIZE, which will store the size of the array (a certain us, the number of elements). On line 13 we declare an array: specify the data type of the, which will be stored in an array of cells, give the name and specify the size in square brackets.
Important, in square brackets, we can only record the entire constant values. It must be either immediately enter an integer between square brackets in the array declaration (int firstArray[100];), or define an integer constant to declare an array and put in brackets the name of this constant (as in our example).
The second method is preferable to use, If during the program you will have to contact several times to an array through a loop. The reason is, that when we announce the loop, in it, you can specify a condition to change the counter valueSIZE.
Just imagine, that we need to change the size of the array with 10 elements on 200. In this case, we have to only just change the value of an integer constant, and thus we automatically default to the new size and value to the array, and in all cycles of the programme.
You can try this example, add any other digit in constant SIZE. And you will see, that the program will work fine - to create an array of many elements, on how you specify, make data and displays them on the screen.
In strings 15 – 19 define loop for. His counter i will serve as an index of array elements. At the very beginning, it is equal to 0 and each step is incremented by one until, until it becomes equal to SIZE – the number of array elements.
Note, in one loop and we will assign different values to the array elements and the next line of appeal to them, to display the data, they store, the screen.
Run the program and see the result:
Assign the value of array elements can be different ways - initialize it when creating or using a loop. If the size of a large array, there is a great opportunity to use a loop for or while to initialize its elements. So we did in our example. You can fill the array with random numbers – this we have a separate article.
And if an array of very small, for example on 5 elements, initialize it can be immediately at the announcement:
So the element with index 0 – firstArray[0] -will be set to 11, and the last element of the array firstArray[4] -value 15. There is a chip-you can not specify the size of the array in square brackets, and make a record:
Previous post equivalent to that. Only in the second case, the compiler will automatically calculate the size of the array, in the amount of data in braces.
When initialization of the array elements, when the array must be cleaned of "garbage" (residual data of other programs in memory) it is better to assign all elements of the value 0. It looks like this:
You should remember, that such initialization is only possible to fill with zeros. If you want to fill the elements of the array to any other numbers, better to use cycle. In C ++ 11 (coding standard) using the list-initialization (initialization with braces) even allowed to drop sign= .
I want to show another reception when creating an array initialization. For example, for an array of 30-minute items we need to make values 33 and 44 only in the cells with index 0 and 1 respectively, and the rest fill with zeros. Then do so:
These data will be included in the zero and the first cell, and the other value will automatically 0.
Organize filling an array you can and using the operator cin:
1 2 3 4 5 | for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) //заполняем и выводим значения на экран { cout << "Введите значение в ячейку №" << i << " :"; cin >> firstArray[i]; } |
To assign or change the value of a specific item, it is necessary to refer to it, using its index. For example, all the values of an array of 500 elements that suit us, but it is necessary to change the value of only one. Then we turn to it by its index : firstArray[255] = 7;
With that sorted out, now let's look, how does the array is located in memory. An array of type int of the five elements will take 20 bytes of memory – 4 bytes (int) * 5 (amount of elements) – and the data will reside in memory sequentially, as shown in Figure:
To summarize and mention the most important of all arrays:
- array declaration syntax :
tip_Dannyh_Massiva array_name [the size];
- array variables are called elements, and each element has its own serial number - index.
- numbering array indexes start at zero!!!
- initialize an array only when it is created – int firstArray[3] = {1, 2, 3}; Initializes later is not allowed:
firstArray[3] = {1, 2, 3};If the array has not been initialized in the beginning, you can assign values to its elements, using loops or simply referring to a desired item by its index.
- initialize an array only when it is created – int firstArray[3] = {1, 2, 3}; Initializes later is not allowed:
- an array can be one-dimensional – such, as discussed in this example, and multidimensional – dvumernыm, three-dimensional ... (they will be discussed in one of our next articles).
Don't forget about the need to practice solving tasks – Tasks: Arrays in C++. Want to learn more about arrays in C ++ (including character arrays and strings)? Watch these video tutorials:
Now I know, just as many similar store data using arrays in C ++. Thank you for the availability of teaching material!
Arrays in c++ – This is what I was looking for!!! Mercy thank you for the work
When I pointed out the most important, it was necessary to specify the, that random access to element of the array is performed in O(1). The text of the article should clarify IMHO, that is the random access provided by the fact, that the size of the array elements and fixed elements are arranged sequentially in memory.
Somehow nice to draw a picture for an example of the type of:
[code]
int a[99];
a[5] = 1; // equivalently (a + sizeof(int) * 5) = 1
[/code]
That is. a reference to element[99999] It happens quickly, as a[2], for example.
Can this be somehow beautifully draw.
It is in many respects the key point, tk. access time – it is one of the key factors of the data structure selection, which include arrays.
unnecessarily. This introductory article, possible to compare arrays with other data structures, very superficial, Without going into the details of the implementation of other structures. View such comparisons can be in books on algorithms, for example, in Skieny.
I would immediately wrote about dynamic arrays. Article generally be removed and would write again. In the article a bunch of mistakes and inaccuracies. With terminology trouble.
Here these preamble, I would have removed:
[quote]
Arrays are extremely important theme in C ++.
Soon will please you - to understand and learn how to use arrays is simple enough even a beginner.
Note the ground and move on to the practical example:
Well, another way to assign values - it is to apply to each element of the array separately.
….
[/quote]
just compare 2 fragment:
[quote]
an array in c ++ is the sum of a certain number of one-type variables, having a name - for example, int array [3];. This entry means, we announced an array named array , which contains 3 int variables;
array variables are called elements ;
Each element has its own unique code - a sequence number. Using the index, we can refer to a specific element. IMPORTANT - based indexing begins with 0. So in an array int array [3] the first element has index 0, and the last - 2. To contact, for example, to the zero element of the array and change its value, it is necessary to specify the name of the array in square brackets to indicate the index – array [0] = 33.
[/quote]
[quote]
array declaration syntax :
tip_Dannyh_Massiva array_name [the size];
looking at the syntax can be defined: array - a certain number of similar data, united by a common name.
array variables are called elements, and each element has its own serial number - index.
the numbering of the elements of the array starts from zero!!!
initialize the array can be either at its creation, or using cycles.
array may be one-dimensional - such, as discussed in this example, and multidimensional - a two-dimensional, three-dimensional ... (they will be discussed in one of our next articles).
[/quote]
>> In string 7 we define an integer constant size, that will keep
In string 7 written “int main”.
Vladimir, thanks for your comments. I think, many will be out of place to check out for more information about arrays.
As for writing articles – guided by beginners in programming and try to write as much as possible available. You, as a person skilled , it certainly seems primitive, but novice programmers will appreciate. Who need more in-depth consideration of the topic, he did not even read a book.
p.s. numbers term – changed.
OK, to a thousand times not to talk:
“the numbering of the elements of the array starts from zero!!!”
simply call the first element zero.
Initialization with braces – this subtlety, which, IMHO, beginners do not really needed. Not all compilers support it. And if the article is focused on students, it is necessary to take into account the, in our universities love to give students all sorts of ancient compilers type BC3.1.
interesting, Why give these universities “antique” compilers, if visual express freely available
not heard that b universities us something imposing old! of course, want to Code::Blocks write, though in Visual Studio, I do not remember when, under that Borland wrote, but remember the old days of hand!!!
funny but remember started with Dev-C ++ aydishki) oh there was a time!
Vladimir, Firstly this site for beginners, so do not be judgmental about everything that is written here! It seems to me, the newcomers there will be the same! It is not necessary here to speak as someone to learn, I think that many will understand. Secondly, If you have comments on the text, or bug fixes – the Orfus you to help, no need to clutter up the chat!
Thirdly, I think the author of the website better know how to express the code, not necessary here to impose their views, how to do that, same obuchalovka for future labor programmers, but not for pros, so that “Initialization with braces - a subtlety, which, IMHO, beginners do not really needed”, I think this text is stupid, it's the subtleties of the language (!), and everything is important, all you need to know, as it is written, that would be in the future in someone else's code is not gawk “And what is this and why”!!!
Good luck! Yes you will arrive in Boost!
So people, Webmaster do not interfere with work!!!_) He himself knows what material is spread… accepted only good advice and comments! Do not forget, you see an error, “BEIT” in Orfus, Ctrl + Enter your to help!!!