To begin to address the tasks, proposed in this article, you need to know that is two-dimensional (multidimensional) arrays . Tasks are arranged from simple to complex. So that, If you're new to programming, start with the first, to better deal with the other.
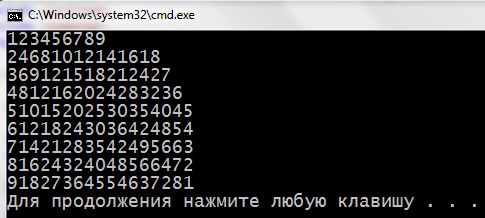
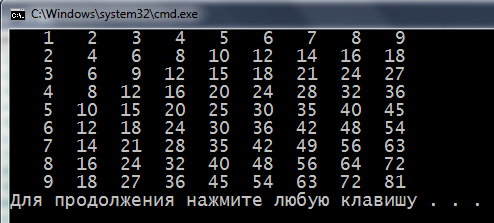
1. Declare a two-dimensional array, fill integers and show on the screen.
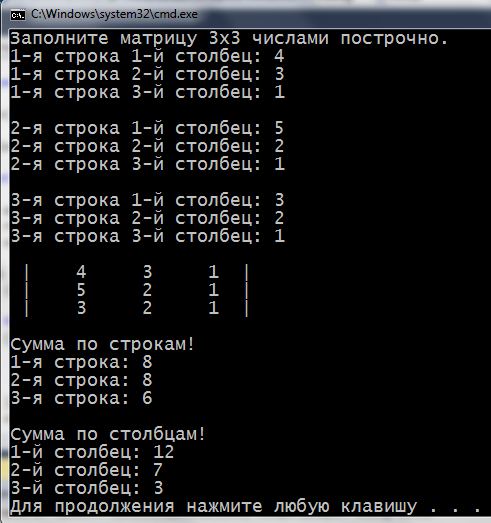
2) Объявить двумерный массив и заполнить его построчно с клавиатуры. После заполнения – показать заполненную матрицу на экран и посчитать сумму элементов отдельно в каждом столбце и каждой строке.
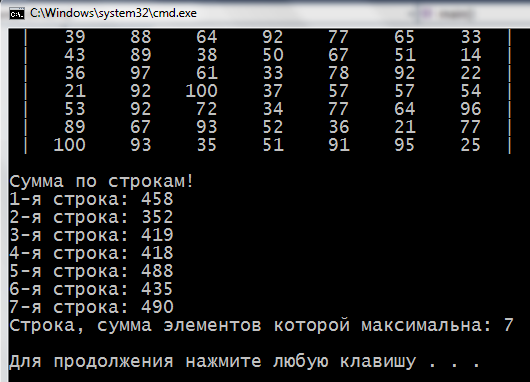
3) Fill two-dimensional array of random numbers 10 to 100. Calculate the sum of the elements separately in each line and determine the line number, in which this sum is maximal.
Your questions, которые возникли при решении задач, leave comments on this article.

Problem No. 3 can be solved using only 1 nested loop, place of three, as in the answer.
You need to attach code to such statements like this
I agree, You shouldn't give such stupid solutions to problems to beginners, including me. We need to train people to use fewer unnecessary loops from the very beginning., to improve program execution speed..
Here is the normal solution to the 3rd task: cpp.sh/9zvl
Stupidity written (about “improve program execution speed”).
1. Tried to solve problem #2, by introducing two constants:
iLine for the number of terms
iColumn per number of columns
that is, the number of rows does not match the number of columns. As a result, after compilation, The wrong value of the sum of the 3rd column is displayed. What is my mistake?
2. In the example of solving problem No. 2 in line of code No. 35, as I understand it, instead of columnSum[rowNum]—— must be —–columnSum[columnNum] or I'm wrong?
IMHO, if the number of rows does not match the number of columns, then you need to create two separate loops to calculate the sum of rows and columns.
had the same problem, that's what I came up with.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, “rus”);
const int strok = 2;
const int stolb = 3;
int array[stroke][stolb] = {};
int isumm[stroke] = {};
you name[stolb] = {};
int s(0), st(0);
cout << "Заполните таблицу"<<endl;
for (int s = 0; s < stroke; s )
{
for (int st = 0; st < stolb; st++)
{
cout << "Введите значение " << s + 1 << "-й стройки и " << st + 1 <> array[s][st];
}
cout << endl;
}
for (int s = 0; s < stroke; s )
{
for (int st = 0; st < stolb; st++)
{
cout <<setw(5)<< array[s][st];
isumm[s]+= array[s][st];
iSum[st]+= array[s][st];
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < stroke; i )
{
cout << i + 1 << "-ая строка cумма " << isumm[i] << " " << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < stolb; i )
{
cout << i + 1 << "-ый столбец cумма " << iSum[i] << " " << endl;
}
return 0;
}
How to fill a rectangular matrix consisting only of zeros and ones , having N rows M columns
Hi. Solved the second problem. everything works as it should. Then I went to look at the solution. Everything is ok there too. BUT. I don’t understand why write the sum of all rows and all columns in arrays when you can write them in variables? What's the point? Here is my solution. Did it without any fancy stuff.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int matrixSize = 3;
int arr[matrixSize][matrixSize] = {};
// Entering a two-dimensional array from the keyboard
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
for(int j = 0; j > arr[i][j];
}
}
// Outputting a two-dimensional array
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
cout<<"\t"<<arr[i][j];
}
cout<<endl;
}
// Calculating and displaying the sum of rows
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
sum += arr[i][j];
}
cout<<endl<<sum;
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
// calculating and displaying the sum of columns
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
sum += arr[j][i];
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
}
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int matrixSize = 3;
int arr[matrixSize][matrixSize] = {};
// Entering a two-dimensional array from the keyboard
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
for(int j = 0; j > arr[i][j];
}
}
// Outputting a two-dimensional array
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
cout<<"\t"<<arr[i][j];
}
cout<<endl;
}
// Calculating and displaying the sum of rows
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
sum += arr[i][j];
}
cout<<endl<<sum;
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
// calculating and displaying the sum of columns
for(int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i )
{
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < matrixSize; j )
{
sum += arr[j][i];
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
}
Why was my code not inserted correctly??
Given a two-dimensional array A of 5 rows and 4 columns. Make a program, which calculates the value of the product of the row sums.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, “ru”);
srand(time(NULL));
const int ROWS = 5;
const int COLS = 4;
int z = 0;
int x = 0;
int ms [ROWS][COLS]{};
int ms2 [ROWS]{};
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i )
{
for (int j = 0; j z)
{
z = ms2[i];
x = i;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i )
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLS; j )
{
cout << ms[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout << "|" << "сумма " << i + 1 << " terms = " << ms2[i] << endl;
}
cout << "максимальное значение у " << x + 1 << " strings – " << from << endl;
}
task No. 1:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, “rus”);
const int RowCount = 3;
const int ColumnCount = 4;
int ourMatrix[RowCount][ColumnCount] = {};
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < RowCount; rowNum )
{
for (int columnNum = 0; columnNum < ColumnCount; columnNum )
{
ourMatrix[rowNum][columnNum] = rowNum + columnNum;
cout << ourMatrix[rowNum][columnNum] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}