 We all got acquainted with three repetition structures in C ++ programming. It loopsfor, while и do while. If you've been paying attention, attachment structures logical choice if and else in the loops have been applied. Now we consider the nested loops – when the body is one loop (external) hosts another loop (internal). Such nested loops in the external loop may be somewhat.
We all got acquainted with three repetition structures in C ++ programming. It loopsfor, while и do while. If you've been paying attention, attachment structures logical choice if and else in the loops have been applied. Now we consider the nested loops – when the body is one loop (external) hosts another loop (internal). Such nested loops in the external loop may be somewhat.
On its structure, nested loops remind me boxes of different sizes, as in our drawing. These boxes can be easily folded into one another and placed in a large box. So with loops. Program, to get to the nested loop, you must first begin any of the outer loop (open the lid of a large box), run, what is written in the code to the inner loop, and then proceed with the implementation of this loop.
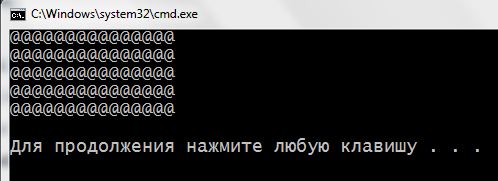
There is one interesting common example, to showcase the work of nested loops. Consider it: using loops, must draw a rectangle of size 5 x 15 of the characters @.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) // этот цикл отвечает за кол-во строк { for (int j = 0; j < 15; j++) // этот - за кол-во символов в каждой строке { cout << '@'; } cout << endl; // переход на строку ниже } return 0; } |
At first it starts loop for in string 6. Since his body nothing is written to the second loop, the program immediately starts executing this nested loop – strings 8 – 11. As a result of its implementation, on the screen are displayed on one line 15 characters @ and it exits. Here work cout in string 12, the control variable i increased by one and continue the implementation of the main and nested loops. That is, again 15 characters on the screen and move to the line below. So it will be done 5 times, after which the program exits. On the screen we see the, that was in the condition:
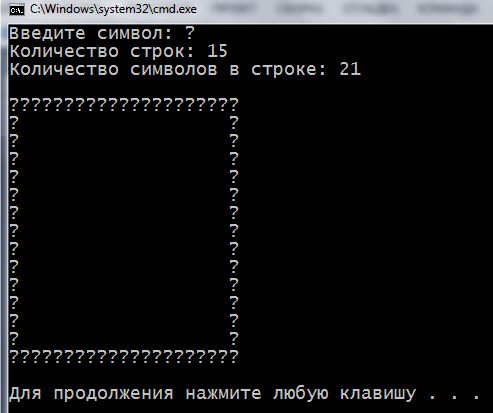
You can slightly complicate the task. Now, let the symbol for printing the user selects pieces, by keyboard input. He chooses the size of the – width and height. Another innovation – the figure should be empty, not filled, as in our previous example. That is, it must consist solely of the contour. Here is our solution:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int lines = 0; int symbInLines = 0; char symbol = 0; cout << "Введите символ: "; cin >> symbol; cout << "Количество строк: "; cin >> lines; cout << "Количество символов в строке: "; cin >> symbInLines; cout << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= lines; i++) { if (i == 1 || i == lines) // 1-я и последняя строка { for (int j = 1; j <= symbInLines; j++) { cout << symbol; // сплошная из символов } } else // все строки между первой и заключительной { cout << symbol; // показать один символ for (int j = 1; j <= symbInLines - 2; j++) { cout << ' '; // пробелы в строке (symbInLines - 2) раз } cout << symbol; // показать ещё один символ } cout << endl; // новая строка } cout << endl; return 0; } |
The result depends on the input, which asks the user. I turned the black square of the issues :)
One more example: print a multiplication table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { for (int f = 2; f <= 9; f++) { for (int s = 1; s <= 9; s++) { cout << f << " * " << s << " = " << f * s; cout << endl; } cout << endl; } cout << endl; return 0; } |
As a result, we see a multiplication table:
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Figures showing only the beginning and the end of the table.
I hope the lesson has been useful for you. Nested constructs in C++ programming are fairly common. Necessarily consider the tasks, we have prepared. If you have any questions on the topic – we are waiting for them in the comments.
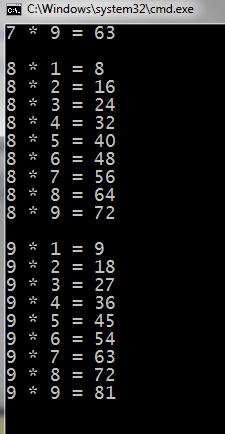
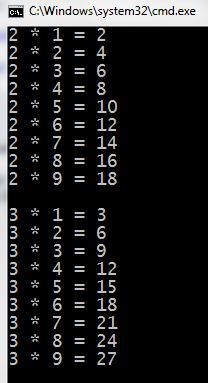
What are the basic rules of their organization?
It's hard to say what you mean by basic rules?
Fundamental rules:
– Cycles should be invested according to the principle “matrjoşki”: each inner loop must be completely ** ** placed inside covering;
– Never change the setting (variable) the outer loop in an internal;
– You never get out of the nested loops operator goto;
Tell, the difference between the principle of nested loops in a C ++ from C #
Basically, nothing more than.
Although C # … it sucks, and to the discussions on this site has nothing to do.
why sucks?
Tell, This solution is an example of your lesson with the square of the symbols, equivalent to your decision is given in lesson? Or your version of all the same has the advantage? If yes then what? Thank you.
Decision any problem can be written in many, often many tens of, different ways.
The criterion for the correctness of the program is only result its implementation – run and make sure.
How do: the user enters a radius and a circle drawn with a radius
P.s. I apologize if there are errors( I was a schoolboy:) )
An identical solution with a choice:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int lines, columns;
char sym;
cout <> sym;
cout <> lines;
cout <> columns;
for (int i = 1; i <= lines; i )
{
for (int j = 1; j <= columns; j )
{
if (j == 1 || i == 1)
{
cout << sym;
continue;
}
else
{
if (i == lines || j == columns)
{
cout << sym;
if (j == columns)
{
break;
}
}
else
{
cout << " ";
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Artyom, How were you able to paste the code into the comments??
to Soldier:
“draw a circle” – it is the task of the field graphics, it does not have any relation to the C ++ programming language, and 100% determined by, What graphic libraries (frameworks: MFC, Qt, GTK, wxWidgets и др.) you use + which operating system.
A friend gave this job to c ++ : )
“a circle” must not “draw” in C++.
“a circle” шt is possible “draw” Only the functions of various graphic libraries … that can be called, including, and from C ++ code.
But directly to C ++ it has nothing to do.
P.S. Pass it on to a friend.
Hello, can answer my question below
How to make
DOUBLE CYCLE:PRINT
******
******
******
who knows how to make it so that, in the task with an empty square, the sides were double?
wrote below
Probably so
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, “rus”);
system(“cls”);
double sredn = 0;
int exit = 0, a = 0, b = 0;
cout << "Введите длину и высоту сторон: " <> a;
cin >> b;
for (int i=0; i < a;i )
{
for (int j=0 ; j < b; j )
{
if ( j == 0 || j==a-1 || j == 1 || j == a – 2)
cout << "q";
else if (i == 0 || i == b – 1 || i == 1 || i == b – 2)
cout << "q";
else cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
how to make
00000
00000
00800
08880
88888