In addition to one-dimensional arrays, you may need for the use of multi-dimensional array (two-dimensional, three-dimensional…). This lesson will be considered two-dimensional arrays. They are the most common, and the rest are extremely rare.
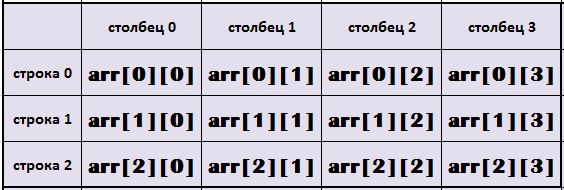
We have already discussed in previous articlesdimensional arrays and C-strings (character arrays).It said, that array elements appear in memory sequentially – element by element. Visually, they can be represented as a single string in the data memory. To access any element of the array, sufficient to indicate the name and index item. The first difference is a two-dimensional array of one-dimensional – its elements comprise two indices: int arr [3][4]; Data of this array can be represented, a table: 3 х 4.
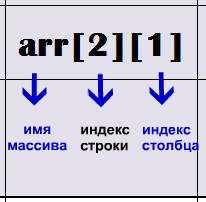
The first index of the array name – This is the index of the string, second – column index.
When you have looked at these pictures, It can be said about the two-dimensional array as – This is an array of, wherein each element as an array. int arr [3][4]; – is an array of 3 elements, each of which is an array of 4 elements.
These two-dimensional array and are arranged sequentially in memory, but by string. First string index 0 – cells from the 0th to 3rd, below the line with index 1 – cells from the 0th to 3rd…
What can store the elements of two-dimensional arrays? For example, You can store the number of parking spaces in the multi-storey car park (6 floors and on each 15 parking places). To do this, declare a two-dimensional array int floorsAndParkings[6][15]; and write in his cell number of seats on each floor. The two-dimensional array can store the C-string. For example: char someStr [3][256]; So we announced an array, that will keep 3 on strings 256 characters each.
Initialization of a two-dimensional array.
Write data to a two-dimensional array, you can declare it. Consider for example parking spaces. Let's say in the parking 2 floor 4 parking space on each. Declare an array and initialize it:
int floorsAndParkings[2][4] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 1, 2, 3, 4 } };
To initialize this looked more readable, arrange it so:
1 2 3 4 5 | int floorsAndParkings[2][4] { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, // инициализация floorsAndParkings[0] { 1, 2, 3, 4 } // инициализация floorsAndParkings[1] }; |
As you remember, According to the standard C + +11, sign= you can miss. Strings are initialized on the same principle:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | char someStr[3][16] { "Двумерные ", "массивы ", "в С++!" }; |
How to display data in a two-dimensional array? You can go a long way and refer to each manual element:
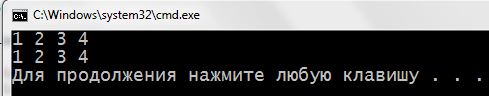
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int floorsAndParkings[2][4] { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 1, 2, 3, 4 } }; cout << floorsAndParkings[0][0] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[0][1] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[0][2] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[0][3] << " "; cout << endl; cout << floorsAndParkings[1][0] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[1][1] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[1][2] << " "; cout << floorsAndParkings[1][3] << " "; cout << endl; return 0; } |
The output of two-dimensional array of C-strings on the screen a little easier, Since we need only specify the array name and the index of the string. Further, the output stream cout alone will display all of the elements of the character array, until it finds '�'
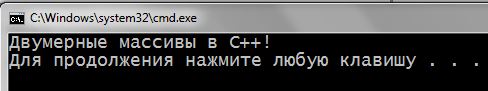
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); char someStr[3][16] { "Двумерные ", "массивы ", "в С++!\n" }; cout << someStr[0]; cout << someStr[1]; cout << someStr[2]; return 0; } |
Good! And if we need to fill an array and display dataint floorsAndParkings[20][100] or char someStr[50][256]? This can be a thankless job ten times to facilitate, using loops. More precisely nested loops.
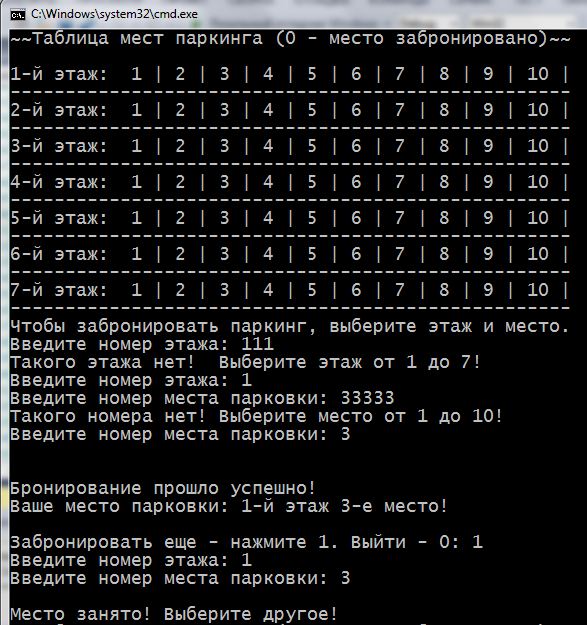
Let's look at an example with parking. Show the user the parking scheme: floors and parking space. To book a place he should choose floor number and seat number. After booking – write value 0 in the appropriate cell, that would mean “the place is busy”.
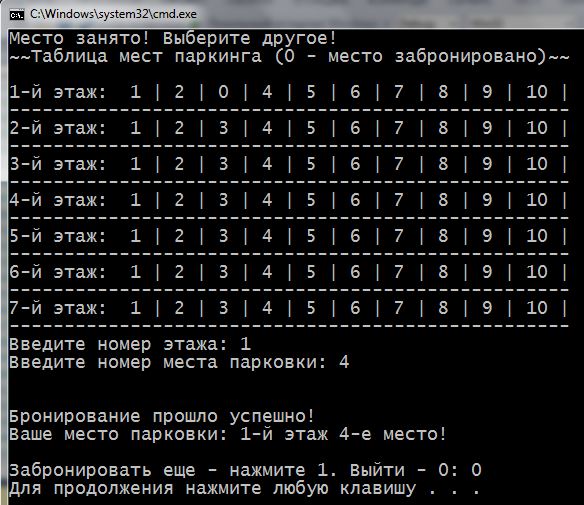
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); const int AMOUNT_FLOORS = 7; // к-во этажей const int AMOUNT_PARKINGS = 10; // к-во парковочных мест на этаже int floorsAndParkings[AMOUNT_FLOORS][AMOUNT_PARKINGS]; // объявление двумерного массива // присвоение значений и отображение cout << "~~Таблица мест паркинга (0 - место забронировано)~~" << endl << endl; for (int f = 0; f < AMOUNT_FLOORS; f++) // используем встроенные циклы { cout << f + 1 << "-й этаж: "; for (int p = 0; p < AMOUNT_PARKINGS; p++) { floorsAndParkings[f][p] = p + 1; // присвоить значение cout << floorsAndParkings[f][p] << " | "; // сразу показать } cout << endl << "---------------------------------------------------" << endl; } int floor = 0; // этаж int parkingPlace = 0; // парковочное место char exit = '1'; // для выхода из do while cout << "Чтобы забронировать паркинг, выберите этаж и место.\n"; do // внешний do while { do // встроенный do while для выбора этажа { cout << "Введите номер этажа: "; cin >> floor; if (floor < 1 || floor > 7) // если такого этажа нет { cout << "Такого этажа нет! Выберите этаж от 1 до 7!\n"; } } while (floor < 1 || floor > 7); do // встроенный do while для выбора места { cout << "Введите номер места парковки: "; cin >> parkingPlace; if (parkingPlace < 1 || parkingPlace > 10) { cout << "Такого номера нет! Выберите место от 1 до 10!\n"; } } while (parkingPlace < 1 || parkingPlace > 10); if (floorsAndParkings[floor - 1][parkingPlace - 1] != 0) // если место свободно { floorsAndParkings[floor - 1][parkingPlace - 1] = 0; // отметить, как забронированное cout << "\n\nБронирование прошло успешно!\n"; cout << "Ваше место парковки: " << floor << "-й этаж " << parkingPlace << "-е место!\n\n"; cout << "Забронировать еще - нажмите 1. Выйти - 0: "; cin >> exit; } else // если место занято (хранит значение 0) { cout << "\nМесто занято! Выберите другое!\n"; // отобразить таблицу, чтобы было видно какие места свободны cout << "~~Таблица мест паркинга (0 - место забронировано)~~" << endl << endl; for (int f = 0; f < AMOUNT_FLOORS; f++) { cout << f + 1 << "-й этаж: "; for (int p = 0; p < AMOUNT_PARKINGS; p++) { cout << floorsAndParkings[f][p] << " | "; } cout << endl << "---------------------------------------------------" << endl; } } } while (exit != '0'); return 0; } |
We used for loop ,in strings 15 – 24, to write data to array and display them simultaneously on the screen. If present this two-dimensional array as a table – the outer loop for passes in the indices of strings– from the 0-s to 6-s. Nested loop – indexes on columns (the cells of table strings) – from 0-s to-9-s.
In strings 32 – 82 is loop do while. His role in, to again and again to offer book your place for car, as long as required to the user. There are two nested loops do while. They implement a variety of floors and parking lot with protection against incorrect input values.
Strings 57 – 81 comprise block if else , which the, in the case of a correct choice of the user displays a message about the successful reservation. If the place is occupied (cell contains a value 0) – notify, it offers a range of floor and repeat the site and displays the updated parking scheme, which marked reserved seats.
It works like this:
continued…
I propose to solve several tasks on the theme two-dimensional arrays.
I recommend to watch the video – Two-dimensional arrays
a1 oil