 It is not always necessary to fill the numericalone-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays serial numbers or specific values. Perhaps, you will need to fill the elements of the array with random numbers. In C ++, there are special fynktsii rand() and srand().
It is not always necessary to fill the numericalone-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays serial numbers or specific values. Perhaps, you will need to fill the elements of the array with random numbers. In C ++, there are special fynktsii rand() and srand().
They are in bibliotechnom file cstdlib, so that their use in the program, you need to connect this library file: #include <cstdlib> or #include <stdlib.h> (for older compilers).
If we use only functionrand() – will receive the same “random numbers” from run to run. Enter the following code and compile the program several times. Note, what “random numbers” there will always be the same.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> // содержит srand() и rand() using namespace std; int main() { int randomDigits[3] = {}; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand(); // запись случайного числа, которое вернет rand() cout << randomDigits[i] << endl; } return 0; } |
A random number is generated in a string 11 and recorded in i-th element of the arrayrandomDigits. In the next string, ask him to show. Starting the program will see each time Only overnight and same numbers:
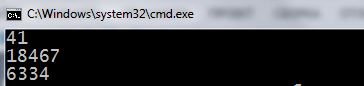 It turns out, that the numbers are generated is not entirely random. In order to achieve “present” random number at restartx program, you must apply the function srand() to function rand(). Thus it is necessary to pass it as a parameter function time() with a parameter NULL: srand(time(NULL)); (parameter or function argument – It `s that, that is written in the parentheses after the function name. When we consider the theme Functions in C ++, talk about this more in detail). In this way srand() It receives as a parameter the current system time, which will be different for each program starting. This will function rand() each time it is to generate random numbers. For use time() you must connect the library file ctime (time.h for older compilers): #include <ctime> .
It turns out, that the numbers are generated is not entirely random. In order to achieve “present” random number at restartx program, you must apply the function srand() to function rand(). Thus it is necessary to pass it as a parameter function time() with a parameter NULL: srand(time(NULL)); (parameter or function argument – It `s that, that is written in the parentheses after the function name. When we consider the theme Functions in C ++, talk about this more in detail). In this way srand() It receives as a parameter the current system time, which will be different for each program starting. This will function rand() each time it is to generate random numbers. For use time() you must connect the library file ctime (time.h for older compilers): #include <ctime> .
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> // содержит time() using namespace std; int main() { int randomDigits[3] = {}; srand(time(NULL)); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand(); cout << randomDigits[i] << endl; } return 0; } |
Try to run. You make sure, now generated different number at each compilation. I have turned this result:
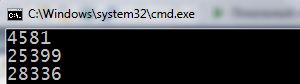
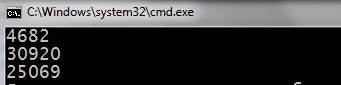
All looks good. Only there is one point: range of random numbers, that are generated in such a way – from 0 to32767. You may need to fill in an array of numbers 200 to 300, from 0.1 to 1, from -20 to 20. This random number generation is possible and easy to implement. Let's look at a few example cases:
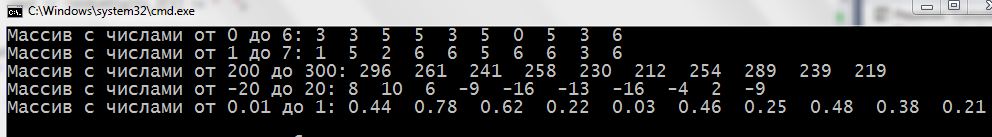
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int randomDigits[10] {}; int randomDigits_2[10] {}; int randomDigits_3[10] {}; int randomDigits_4[10] {}; float randomDigits_5[10] {}; // для чисел c плавающей точкой srand(time(NULL)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand() % 7; // 0 ... 6 randomDigits_2[i] = 1 + rand() % 7; // 1 ... 7 randomDigits_3[i] = 200 + rand() % 101; // 200 ... 300 randomDigits_4[i] = rand() % 41 - 20; // -20 ... 20 randomDigits_5[i] = 0.01 * (rand() % 101);// 0.01 ... 1 } cout << "Массив c числами oт 0 до 6: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 1 до 7: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_2[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 200 дo 300: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_3[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт -20 до 20: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_4[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 0.01 дo 1: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_5[i] << " "; } cout << endl; return 0; } |
In the first the for loop random number generation happens certain ranges and their entry in the appropriate arrays. In each step of the cycle will generate new random numbers. Perhaps someone is difficult to understand how it happens. Let us consider in detail:
rand() % 7 – rand() it generates a number of further evaluated remainder of the division at 7 of that number. Clear, it may be of only From 0 to 6. For example generated 50 – the remainder of the division by 7 is equal to 1, generated 49 – the remainder of the division by 7 is equal to 0.
1 + rand() % 7 – very similar to the previous case, only 0 we will not see, and here 7 It will be in the range. eg generated 49 – the remainder of the division by 7 is 0 and adds one to it, generated 6 – the remainder of the division by 7 is 6 and again added unit.
200 + rand() % 101 – give us a number from 200 to 300. For example generated 100 – the remainder of the division by 101 is 100 and added 200. We get the number of 300. Is generated 202: 200 + (202 % 101)= 200 + 0 = 200.
rand() % 41 - 20 – from the – 20 to 20. For example generated 1: (1 % 40) – 20 = 1 – 20 = -19; generated 30: 30 – 20 = 10.
0.01 * (rand() % 101) – from the 0.01 to 1. For example generated 55: 0.01* 55 = 0.55.
Result:
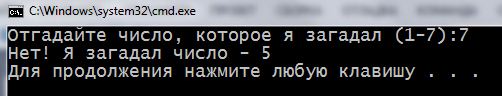
To practice, try to solve the problem: a computer“thinks of” number from 1 to 7, a user has to guess it. If it does not work out – see our variant solutions:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int randomDigit = 0; int version = 0; srand(time(NULL)); randomDigit = 1 + rand() % 7; cout << "Отгадайте число, которое я загадал (1-7):"; cin >> version; if (version == randomDigit) { cout << "Дa! Я загадал число - " << randomDigit << endl; } else { cout << "Нет! Я загадал число - " << randomDigit << endl; } return 0; } |
Tasks with rand() there is an article Tasks: Arrays in C++. Take some time and watch the video:
will go, but bad written about srand. he had “accident” will not improve. Numbers in any case not random, and generates deterministic algorithm. hood “PRNG algorithms”.
Does anyone have a PRNG “fuse” – it is the first number, on the basis of which all others are calculated. And srand() initiates the primer, The default is zero, probably.
unity
>> Try to run. You make sure, now generated different number at each compilation.
Compiling nothing to do with.
>> To practice, try to solve the problem. Computer "thinks of" From the number of 1 to 7, a user has to guess it. If it does not - see our alternative solutions:
A task I would somehow singled out – in a separate paragraph and italic. Your decision would hide under spoiler.
Almost done, as you said )
#include#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
int i = 1+rand()%7;
int j;
for(;;)
{
cout << j;
if (j==i)
break;
else if(j>i)
cout << "Your number anymore" << endl;
else
cout << "Your number is less" << endl;
}
cout << "You guesses it!";
return 0;
}
My version!
#include#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(0, "");
int a = 0;
int c = 0;
srand(time(NULL));
c = 1 + rand() % 7;
cout << "загадано число от 1 до 7. Отгадайте его." <> a;
for (int i = 0;; i++)
{
if (a == c)
{
cout << "Вы угадали, загаданное число:" << a << "\n";
break;
}
else if (a 7)
{
cout << "Число не корректное. Введите число от 1 до 7" <> a;
continue;
}
else
{
cout << "Вы не угадали, загадано число: " << c <> a;
c = 1 + rand() % 7;
}
}
return 0;
}
I Do not connect the library you want but I still worked like you, why?
#includeusing namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus");
int random_digits[3] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
random_digits[i] = rand();
cout << random_digits[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
What is this garbage? we're kind of like 2 + 2 = 4 study. what kind of codes? then more than half do not understand, and we do not pass. is a later lesson, what broke the order?
excuse me. broke.
In order of lessons published on the home page: https://purecodecpp.com/
Good day!
1. With user “Henry Morgan” I agree, why all the topics were divided into sub-categories? It was a bit inconvenient.
2. Prompt, can not understand, I need to make a play dice. Stalknulsya the problem of automatic randomization, the code below:
#include#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus");
char player1 [20] = "";
char player2 [20] = "";
float player1_score = 0;
float player2_score = 0;
int player1_choose = 0;
int player2_choose = 0;
cout << "Введите имя 1 игрока: " <> player1;
cout << "Введите имя 2 игрока: " <> player2;
for (;;)
{
srand(time(0)); // рандомизация генератора случайных чисел
cout << "Нажмите любую клавишу для начало игры. \n";
player1_choose = 1 + rand() % 11;
cout << "Игроку " << player1 << " выпало " << player1_choose << endl;
cout << "Нажмите любую клавишу для начало игры. \n";
player2_choose = 1 + rand() % 11;
cout << "Игроку " << player2 << " выпало " << player2_choose < player2_choose) // ПОДСЧЕТ СЧЕТА
{
player1_score = player1_score + 1;
}
else
{
player2_score = player2_score + 1;
}
/* if (player1_score == player2_score)
{
cout <= 10 || player2_score >= 10) // ПРОВЕРКА ОКОНЧАНИЯ ИГРЫ
{
cout << "Игра окончена со счетом: ";
cout << player1_score << ":" << player2_score << endl;
break;
}
}
}
Lessons in theory should already be in the order from simple to complex. There were moments, but we we have to fix them. If you notice a discrepancy – write.
The code will look later. otpishus
1. when you are writing “can not understand” – you need to start from, what to write what the problem is: not debug the same for you all your code?.
2. In addition, have you got there yet whole 2 additional problems, but not the software, and mathematical properties:
– must not instead of 2 random variables [1…6] take 1-random value [1…12] – the amount of 2-uniformly distributed random does not have a uniform distribution;
– You can not take the rand() % 11 as a random value [0…11] – it's you junior figures accidental, that is not uniform random (and even it is your value – in the range [0…10], but not [0…11] as it was required).