 It is not always necessary to fill the numericalone-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays serial numbers or specific values. Perhaps, you will need to fill the elements of the array with random numbers. In C ++, there are special fynktsii rand() and srand().
It is not always necessary to fill the numericalone-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays serial numbers or specific values. Perhaps, you will need to fill the elements of the array with random numbers. In C ++, there are special fynktsii rand() and srand().
They are in bibliotechnom file cstdlib, so that their use in the program, you need to connect this library file: #include <cstdlib> or #include <stdlib.h> (for older compilers).
If we use only functionrand() – will receive the same “random numbers” from run to run. Enter the following code and compile the program several times. Note, what “random numbers” there will always be the same.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> // содержит srand() и rand() using namespace std; int main() { int randomDigits[3] = {}; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand(); // запись случайного числа, которое вернет rand() cout << randomDigits[i] << endl; } return 0; } |
A random number is generated in a string 11 and recorded in i-th element of the arrayrandomDigits. In the next string, ask him to show. Starting the program will see each time Only overnight and same numbers:
 It turns out, that the numbers are generated is not entirely random. In order to achieve “present” random number at restartx program, you must apply the function srand() to function rand(). Thus it is necessary to pass it as a parameter function time() with a parameter NULL: srand(time(NULL)); (parameter or function argument – It `s that, that is written in the parentheses after the function name. When we consider the theme Functions in C ++, talk about this more in detail). In this way srand() It receives as a parameter the current system time, which will be different for each program starting. This will function rand() each time it is to generate random numbers. For use time() you must connect the library file ctime (time.h for older compilers): #include <ctime> .
It turns out, that the numbers are generated is not entirely random. In order to achieve “present” random number at restartx program, you must apply the function srand() to function rand(). Thus it is necessary to pass it as a parameter function time() with a parameter NULL: srand(time(NULL)); (parameter or function argument – It `s that, that is written in the parentheses after the function name. When we consider the theme Functions in C ++, talk about this more in detail). In this way srand() It receives as a parameter the current system time, which will be different for each program starting. This will function rand() each time it is to generate random numbers. For use time() you must connect the library file ctime (time.h for older compilers): #include <ctime> .
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> // содержит time() using namespace std; int main() { int randomDigits[3] = {}; srand(time(NULL)); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand(); cout << randomDigits[i] << endl; } return 0; } |
Try to run. You make sure, now generated different number at each compilation. I have turned this result:
All looks good. Only there is one point: range of random numbers, that are generated in such a way – from 0 to32767. You may need to fill in an array of numbers 200 to 300, from 0.1 to 1, from -20 to 20. This random number generation is possible and easy to implement. Let's look at a few example cases:
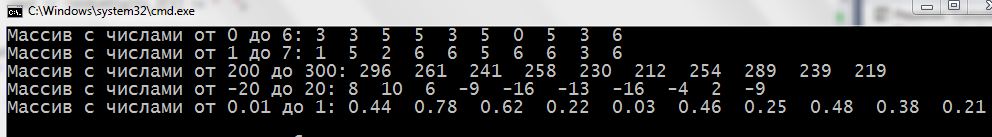
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int randomDigits[10] {}; int randomDigits_2[10] {}; int randomDigits_3[10] {}; int randomDigits_4[10] {}; float randomDigits_5[10] {}; // для чисел c плавающей точкой srand(time(NULL)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { randomDigits[i] = rand() % 7; // 0 ... 6 randomDigits_2[i] = 1 + rand() % 7; // 1 ... 7 randomDigits_3[i] = 200 + rand() % 101; // 200 ... 300 randomDigits_4[i] = rand() % 41 - 20; // -20 ... 20 randomDigits_5[i] = 0.01 * (rand() % 101);// 0.01 ... 1 } cout << "Массив c числами oт 0 до 6: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 1 до 7: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_2[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 200 дo 300: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_3[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт -20 до 20: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_4[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "Массив c числами oт 0.01 дo 1: "; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << randomDigits_5[i] << " "; } cout << endl; return 0; } |
In the first the for loop random number generation happens certain ranges and their entry in the appropriate arrays. In each step of the cycle will generate new random numbers. Perhaps someone is difficult to understand how it happens. Let us consider in detail:
rand() % 7 – rand() it generates a number of further evaluated remainder of the division at 7 of that number. Clear, it may be of only From 0 to 6. For example generated 50 – the remainder of the division by 7 is equal to 1, generated 49 – the remainder of the division by 7 is equal to 0.
1 + rand() % 7 – very similar to the previous case, only 0 we will not see, and here 7 It will be in the range. eg generated 49 – the remainder of the division by 7 is 0 and adds one to it, generated 6 – the remainder of the division by 7 is 6 and again added unit.
200 + rand() % 101 – give us a number from 200 to 300. For example generated 100 – the remainder of the division by 101 is 100 and added 200. We get the number of 300. Is generated 202: 200 + (202 % 101)= 200 + 0 = 200.
rand() % 41 - 20 – from the – 20 to 20. For example generated 1: (1 % 40) – 20 = 1 – 20 = -19; generated 30: 30 – 20 = 10.
0.01 * (rand() % 101) – from the 0.01 to 1. For example generated 55: 0.01* 55 = 0.55.
Result:
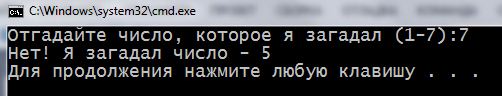
To practice, try to solve the problem: a computer“thinks of” number from 1 to 7, a user has to guess it. If it does not work out – see our variant solutions:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int randomDigit = 0; int version = 0; srand(time(NULL)); randomDigit = 1 + rand() % 7; cout << "Отгадайте число, которое я загадал (1-7):"; cin >> version; if (version == randomDigit) { cout << "Дa! Я загадал число - " << randomDigit << endl; } else { cout << "Нет! Я загадал число - " << randomDigit << endl; } return 0; } |
Tasks with rand() there is an article Tasks: Arrays in C++. Take some time and watch the video:
“randomDigits_5[i] = 0.01 * (rand() % 101);// 0.01 … 1”
Is the range of values is not from 0 to 1?
randomDigits_5[i] = 0.01+0.01 * (rand() % 100);// 0.01 … 1
In the first case, the range [0…1], second [0.01…1].
Good day!
Explain, please, which means that's the record:
“generated 6 - The remainder of the division by 7 is 6 and again added to the unit.”
How did, that the remainder of the division by 7 is 6?
Thank you very much in advance!
Result integer operations: 6 / 7 = 0, and 6 % 7 = 6 …
Same, how, for example: 3 / 7 = 0, and 3 % 7 = 3
Preparation of the generator in the range [0…n] Modulo: rand() % ( n + 1 ) – in some cases bad style. logic, in general, this:
– if consecutively random numbers you need for modeling, Monte Carlo, etc., when you want to save uniform distribution, We use change range scale: long m = ( (long)rand() * ( n + 1 ) ) / RAND_MAX (long is necessary in order to avoid overflow in the multiplication);
– if you need separate random values for other purposes, you can use rand() % ( n + 1 );
About the same can check out the details in a new book “Programming. Introduction to the profession.”, str.. 413:
http://www.stolyarov.info/books/pdf/progintro_vol2.pdf
and do not tell me, But if I have a function, which generates a random number from [0,n] to me it is necessary to somehow change, that she generated s.ch. in the range [0,k] where k>n, that is, with a smaller range than there are all-clear. but how to increase the range, Multiplication does not work, lost part of terms, with the addition of the same situation…
About “is a function of, which generates a random number”.
No you have no such other function, in C you only have the function libraries, which generates a number [0…RAND_MAX) (note, that the larger end of the range “open” – never fall number RAND_MAX, only RAND_MAX – 1). This a very large number!
About “convert to a range of” (let us say [0…K) ):
– bad way: rand() % K
– good way: rand() * K / RAND-MAX (but beware of overflows!)
thank you very much for the answer.
However, the task of which I formulated in the comments above, It does not refer to a specific programming language. Just an abstract problem, is it possible to increase the range generated by a function S.Ch., or whether the act is bijective, and this method is not?
Any problem in programming can not be “at all”, It can only be specific.
A method to increase the range there:
long long rnd = ( rand() * RAND_MAX ) + rand();
Good day!
Could you, you are welcome, explained, why to the remainder of the modulus is necessary to add one?
I see, do not do this – and the number will be generated, beyond the desired range of values.
But I do not know, how to explain mathematically…
Thank you in advance!
The final task, if not add unit during generation of the random number ( randomDigit = 1 + rand() % 7;) – in randomDigit I will record the number of 0 to 6 inclusive. And in the condition required number in the range 1 to 7.
For example:
– rand() generates a number 7: 7 % 7 = 0
– rand() generates a number 13: 13 % 7 = 6
Therefore,, to comply with a specified condition, we add to the calculation of 1.
help with the task.
Create any function to the sort of direct selection and array:(
https://purecodecpp.com/archives/2821
Hello! Dali job, create a simulator. The cycles of more or less figured out, but with integrated graphics can not. Share the link to this topic, on your website can not be found.( The work should be done in dev-cpp , use #include. ,thank you in advance!
Do you want to fulfill your homework INSTEAD you?
Then you here: https://purecodecpp.com/archives/2821
Please tell me what's the problem does not display a numeric array to a file
because, that your << randomDigits_5[10000] – this is:
– не вывод "числового массива", and attempt to display the entire only one array element…
– and even here the wrong: [10000] – 10001 is the first element (Indexing starts at 0) array dimension 10000 …
– the output element of the array – it is a gross error.
Thank you