 In modern life, it is very difficult to do without arithmetic operations. We constantly have something to consider: fold, multiply, subtract, share, etc.. Programming – not an exception. you in 99.9% cases have to use them, when writing your programs. They should not be afraid of – all arithmetic operations – easy, understandable and familiar to us from school.
In modern life, it is very difficult to do without arithmetic operations. We constantly have something to consider: fold, multiply, subtract, share, etc.. Programming – not an exception. you in 99.9% cases have to use them, when writing your programs. They should not be afraid of – all arithmetic operations – easy, understandable and familiar to us from school.
Consider the arithmetic operation in the following table.
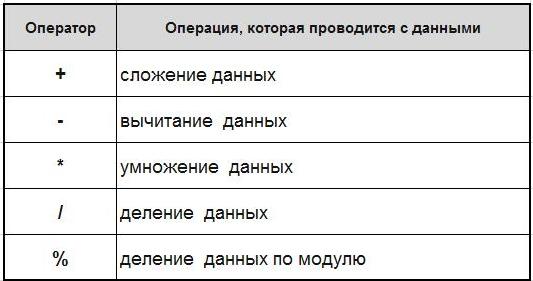
Here, particular attention should be paid to the modulus (%). This operation is often used in solving various tasks. An example of its application: if we need to divide modulo 9 on 4 (9 % 4), the result is 1 (this residue – then, What's on 4 It is no longer divided into whole). More examples: 20 % 8 = 4 ( 8 placed in the 20 2 fold: 8 * 2 = 16, 20 – 16 = 4 remainder of the division ), 3 % 2 = 1, 99 % 10 = 9, 9 % 10 = 9. Important:
- modulo division applies only to integer variables ;
- can not be divided according to the module 0;
Example:
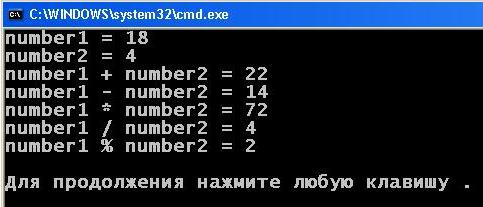
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int number1 = 18; int number2 = 4; cout << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; cout << "number2 = " << number2 << endl; cout << "number1 + number2 = " << number1 + number2 << endl; cout << "number1 - number2 = " << number1 - number2 << endl; cout << "number1 * number2 = " << number1 * number2 << endl; cout << "number1 / number2 = " << number1 / number2 << endl; cout << "number1 % number2 = " << number1 % number2 << endl; cout << endl; return 0; } |
Here you can see, the fission num1 on num2, it appeared on the screen only the integer part of – 4 (although the exact value 4.5). The fractional part is cut, because the variables are defined, as integer – int. As a result of the modulo we see 2 – what is left in the remainder of the division 18 on 4.
Another thing I would like to consider in this article – so-called combined (or compound) statements. In addition to its role of arithmetic, they simultaneously act as a variable assignment. Here is a list of composite statements:
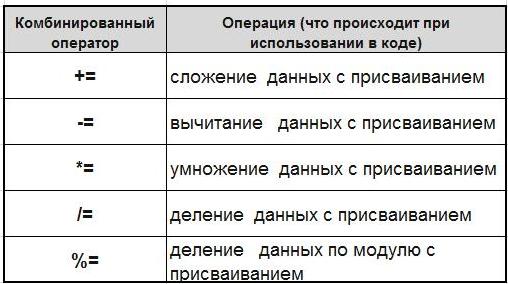
Illustrate:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { setlocale(LC_ALL, "rus"); int number1 = 10; int number2 = 4; cout << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; cout << "number2 = " << number2 << endl; number1 += number2; // эквивалентно записи number1 = number1 + number2 cout << "Результат от += : " << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; number1 -= number2; // number1 = number1 - number2 и т.д. cout << "Результат от -= : " << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; number1 *= number2; cout << "Результат от *= : " << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; number1 /= number2; cout << "Результат от /= : " << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; number1 %= number2; cout << "Результат от %= : " << "number1 = " << number1 << endl; cout << endl; return 0; } |
Although for someone, at first sight, these statements may seem confusing, trust, to them very quickly and you can get used to successfully apply in their programs. You just need some practice with their use. Your code will be more compact look. Same, the use of combined statemants is a sign of good programming. Therefore,, Though not an error in the code separately from the use of the addition assignment – number1 = number1 + number2;, preferable to use a shortened version of the recording number1 = number2;
Result:
In this article only examined binary statements – those which are used for arithmetic operations with two variables (operand). In one of the following, we look at unary statemants (for operations on one variable) – increment and decrement, and next – and ternarnım statement (which requires three operands).
It is desirable to consolidate the knowledge acquired practice – Tasks: Arithmetic operations in C ++
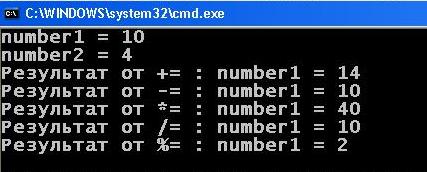
super, enough available all painted! It is only necessary to pay attention that a simple binary statement type ” + ” It is doing simple addition, and an integral type binary statament ” += ” apart from the addition of (or straight.) More and assigns the value of the first variable (in this case number1) each time when calculating…
thanks to the author!
Thanks! Now I will learn to use arithmetic operations
And I liked it, I understand everything perfectly, there are binary statements, They are used for two variables, say in your example: number1 = number2; there are two variables, binary means, and there is the unary ternary, Here is an example of a unary: 34++ or 23–, and maybe so: ++34 or –23; Example ternarnogo: ? first statement : the second statement. General thank you for everything, I will continue to study
Thank you for the course!
Explain why it is wrong produces results “-=” and “/=”?
Operations carried out all right. Share your results, if you do not like this.
At the = sign can be used any binary operations … for example:
=&& , =| , =% , =<> …
And still it gives correct results … Only they must be correctly interpreted (that should have).
we must not forget that the value of variable number1 varies with each operation.
It's simple. You each time assigns 1 a new value, without changing the old. Simply check the sequence again.
I did not get an error in the iostream
complete garbage dumbest website.
well, like this “shit” – it shit in Africa … : pass by, keep moving!
Everything is very accessible and understandable, thank you very much for the lessons.
how to implement the operation “modulo” for numbers in float format, long float или doublе???
For real numbers such as the operation “modulo” It does not make sense and is not defined.