Getting to the solution of tasks, read articles Arrays in C++ and The random number generator rand(), if you have not read them. Try to address the proposed tasks independently and watch our decisions only in extremis.
1. Create an array of type int on 10 elements and fill it with random numbers from 7 to 14. After filling overwrite all numbers, who for more than ten: from the stored value to take away 10. For example the number is stored in the cell 12: 12 – 10 = 2. Write to this cell 2 Writing the new value, use composite(combined) statements.
2. To fill an array of elements 50 odd numbers from 1 to 99. (use the operation remainder of the division, to check on the number of parity)
3. Declare three arrays. The first two to fill with random values from 10 to 30. In the third elements of the array to record the amount of the corresponding elements of the first two sets. (in the third cell zero – the sum of zero cells first and second arrays, and so on). Then, find the arithmetic mean of the elements of the third array, the maximum value and minimum value, which it holds.
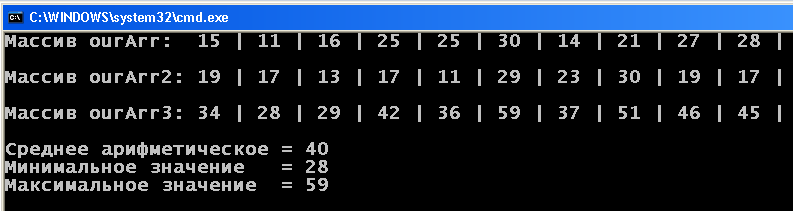
sorry!for not properly a question, there is a solution to 3 her task by one-dimensional array, where you can display the code, so that you can check and point out flaws?
What for?
This is not an elementary school, no one to watch your code will not be.
And the comments here are not adapted and distort code, if you enter it here.
A criterion of code quality for you always must be of execution program: if they comply with the conditions imposed, then everything is fine.
the university is looking code
A typical cattle-programmer.
ideone.com
ATP for an answer.
Tell me please, what's my mistake (outputs the minimum value 0)
I found another way)
what a moron I…
When we are looking for an average value, This same float? If that, then 3 the task bug. Although she is not significant, but I think, it is not a good habit to round))
This rough error:
– averageValue variable must be declared as a float / double (better double);
– averageValue expression calculation should be rewritten as, to calculate with real values, like this:
averageValue = (double)sum / SIZE;
2 the problem is not resolved correctly?
that's the same
#include
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){
int arr[50] = {};
for (int i = 0; i<50; i ){
do
arr[i] = 1 + rand() % 100;
while (arr[i] % 2 !=1);
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}